Abstract
Background/Aims: Individuals with sickle cell disease (SCD) are at high risk for vitamin D deficiency due to dark skin color, limited physical activity, poor nutrition, and renal dysfunction. In smaller retrospective studies, vitamin D deficiency in SCD was associated with increased frequency of acute pain events and higher opioid use, however the impact of vitamin D deficiency on pain related patient reported outcomes has not been described . Supplementation with high dose vitamin D is shown to be associated with fewer pain days per week and higher physical activity scores in patients with chronic pain. Thus, the objective of our study was to evaluate relationship between vitamin D levels, acute health care utilization and self-reported pain among children with SCD. We hypothesized that vitamin D deficiency is associated with increase health care utilization for pain and patient-reported outcomes for pain.
Methods: Patients with SCD (1 to 18 years of age), enrolled in Sickle Cell Clinical Research and Intervention Program (SCCRIP), at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital were included in the study (Hankins et.al., Pediatric Blood and Cancer, 2018). Demographic, clinical and laboratory data were extracted from SCCRIP database. Prospective pain event leading to a hospital visit was analyzed. We analyzed pain-related hospitalizations in two ways: the number of pain-related hospitalizations within 2 years prior to and after vitamin D measurement in a cross-sectional design and longitudinally. Generalized linear regression model was used to examine associations between vitamin D and cross-sectional pain events with adjusting for hydroxyurea use. Generalized linear mixed effect model was used to assess the associations between vitamin D and longitudinal pain events, with adjusting for SCD genotype, sex, age, hydroxyurea use and interaction between age and hydroxyurea use.
Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory™ Sickle Cell Disease Module (PedsQL™ SCD) was used to measure pain and pain interference using 1) Pain and Hurt and 2) Pain Impact scales. PedsQL™ SCD assessments include a Likert response scale. Items are reverse -scored and transformed to a 0-100 scale where higher scores indicate better health related quality of life in that scale. Two sample t-test or Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to compare mean scores between the two groups.
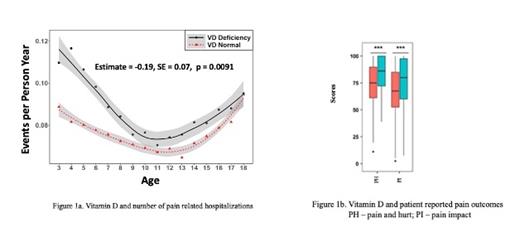
Results: A total of 799 patients (females, n=398; males, n=401) were included in the study. Mean age (Standard Deviation [SD]), range at time of first vitamin D measurement for entire cohort was 8.7 (4.7), (0.8-18 years). Mean (SD) initial vitamin D level for entire cohort was 19.0 (9.4) ng/dl. Mean (SD) number of pain-related hospitalizations within two years of first vitamin D measurement was higher in the vitamin D deficient group as compared to non deficient group [0.81(1.97) vs 0.66 (1.2), (p=0.0034)]. Longitudinal data analyses showed vitamin D deficiency was associated with increased number of pain related hospitalizations (p=0.0091), after adjusting for covariates listed above (Figure 1a).
Mean (SD) scores for Pain and Hurt in vitamin D deficient versus non deficient group were [74.5.7(18.2) versus 83.5(15.6), p < 0.001]. Mean (SD) scores for Pain Impact in vitamin D deficient group as compared to non deficient group were [(66.7 (22.7) versus 75.5 (22.3), p <0.001] (Figure 1b)
Conclusion: Results indicated that low vitamin D levels predicted higher frequency of painful events leading to a hospital visit and were associated with higher prevalence of self-reported pain and pain interference. Further studies evaluating mechanisms by which vitamin D influences sickle cell pain are warranted and larger controlled trials can help evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of vitamin D for sickle cell pain.
Hankins: UpToDate: Consultancy; Bluebird Bio: Consultancy; Vindico Medical Education: Consultancy; Global Blood Therapeutics: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal